Use of tires as shock absorbers?

Used tires can be built into house foundations to work as low cost base isolators and provide shock absorption in earth quakes. Used tires don’t have much value in the informal sector and are usually dumped in the open. There they enable mosquito breeding with subsequent malaria, dengue and zika risks. Consequently environmental synergy effects can be achieved if used tires can be recycled in common house construction.
In practically all harbors you can see old tires hanging on the quay sides as fenders to mitigate the shock if a ship hits the dockside.
In races, piles of tires are protecting spectators from crashing vehicles.
When blasting rocks in open air, mat assemblies of cut tires are used to protect against undesired destruction effects.


The Elephant Foot
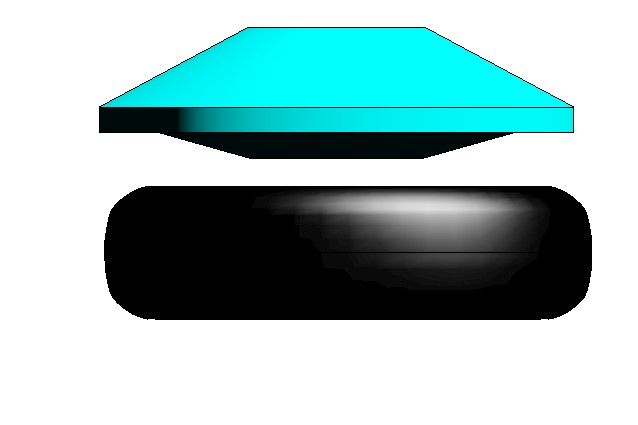
The concept is based on low cost construction techniques: old and worn out steel belted tires plus small quantities of concrete. In the bottom of the foundation ditches round river stones are placed to work as roller bearings. The tires are then placed side by side (without filling) to provide the elastic shock absorbing response. The Elephant Foot made of regular concrete is merged into the foundation tie beam via protruding reinforcement bars. The cone shape will make the structure center back after the quake.
Shake table test Guwahati, India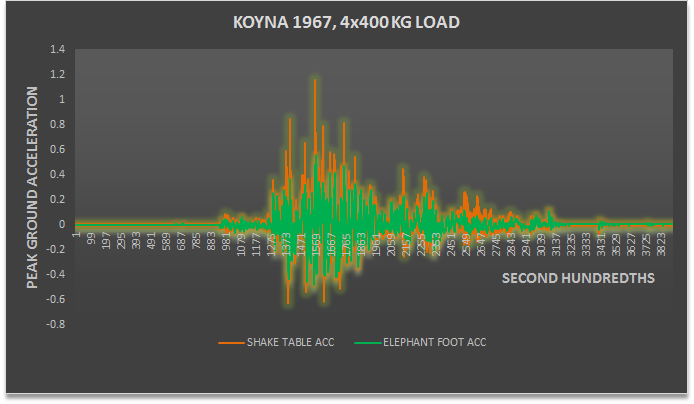
The concluding shake table tests February 2016 at the Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati have been evaluated by Prof James Kelly, Dept of Civil Engineering, UC Berkeley.
Evaluation UC Berkeley
Watch Youtube:
http://youtu.be/qvvUfwdXndo